Teleradiology is a specialty within telemedicine. Since medical imaging is a widely-used and primary diagnostic tool in medicine today, teleradiology is one of the most relevant aspects of telemedicine. By sharing high-quality digital medical images across locations, patients can receive a faster diagnosis, doctors can collaborate, and hospitals can lower the cost of delivering high-quality medical care. Teleradiology is widely used today in clinics and hospitals throughout the world.
What Is teleradiology?
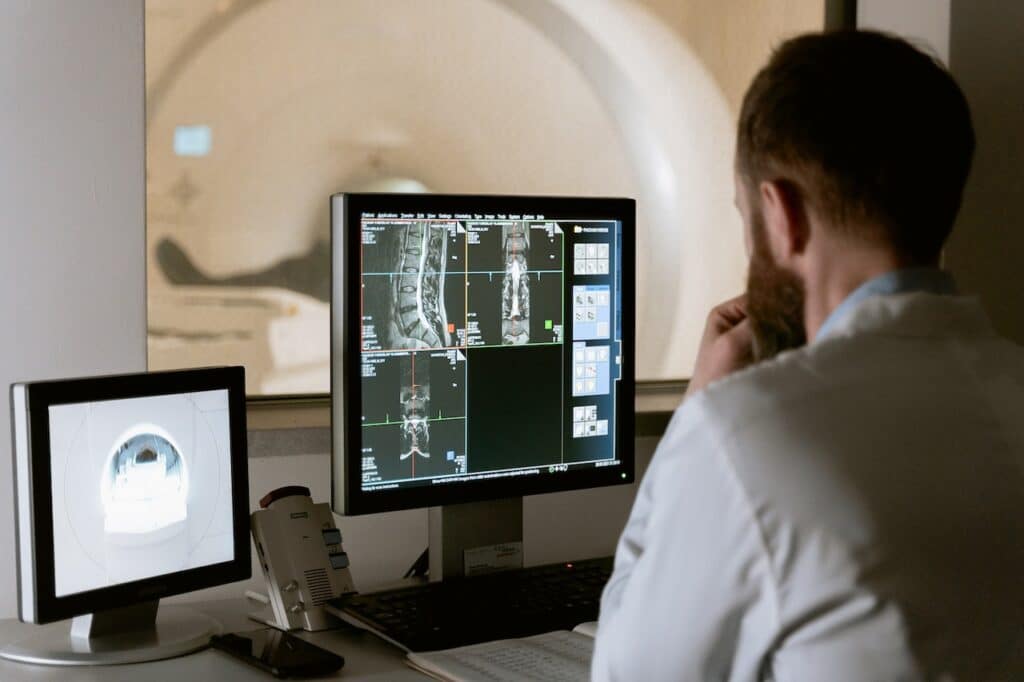
Teleradiology is a niche within telemedicine specific to imaging. Thanks to teleradiology, medical images —CT scans, x-rays, MRI scans, etc.— are shared across locations through telecommunications technology, enabling medical professionals in a different location from the patient to view and evaluate the images.
In addition to the imaging equipment and medical professionals needed for all medical imaging, teleradiology relies on a triad of technology. It requires first of all an image upload station at the site where the images are taken; second, a transmission network to share the images; and finally, an image viewing station at the off-site location where a qualified physician will view the images. As complicated as it sounds, with the right software to integrate the system, it is actually as easy as sending an email.
What Are the Advantages and Benefits of Teleradiology?
With teleradiology, medical facilities can save costs and diagnose patients more quickly, and doctors across the globe can collaborate for patient care, research and training.
Radiology is a specialty in high demand and, as a result, there is a shortage of radiologists. When the radiology patient load exceeds the capacity of a medical facility to read images in an adequate time frame, hospitals can connect with radiologists in other locations to request support. They can also take advantage of teleradiology to connect with radiologists in distant time zones to cover off-hours radiology needs, such as night time hours in urgent care and emergency rooms. This is especially helpful for hospitals and clinics in rural areas. With teleradiology, these hospitals can fill in any existing gaps in radiology expertise to provide adequate imaging reads times as well as facilitate patient diagnosis and treatment.
Additionally, as radiology has become increasingly specialized and subspecialties have emerged, there is a higher demand for specialist readings. But these specialists may not be available at every hospital. Through teleradiology, specialized radiologists can offer their expertise easily across locations to the benefit of many patients.
Moreover, through teleradiology, physicians and specialists across the globe can also easily collaborate for any reason: research, clinical trials, tumor boards, education, and so on.
Specialized radiologists can even work from a home office by using web-based image viewers to provide their expertise to various locations.
As telemedicine continues to become accepted by both patients and physicians, the applications and advantages of teleradiology will only become more evident.
What Are Some Examples of Teleradiology Applications?
Teleradiology is used for diagnostic purposes, virtual tumor boards, clinical research, collaboration, second opinions, and ongoing education.
Patient diagnosis is one of the most common applications of teleradiology. Radiology reads are key in patient diagnosis. Faster read times and the ability to quickly access specialized radiologists and other professionals leads to quicker patient diagnosis and treatment. Through teleradiology, patients can more easily obtain a second opinion, and doctors can collaborate on difficult cases, which improves the quality of patient care.
Through teleradiology, virtual tumor boards can also be established. With the ability to share radiology images, medical professionals in distinct locations can work together as a tumor board to review images of tumors and discuss advanced treatment options.
Ultimately, teleradiology allows medical professionals and researchers to work together virtually. When images can be easily shared across locations, they can collaborate on research, clinical trials, and hold continuing education seminars for medical professionals around the globe.
What Types of Images Are Normally Used in Teleradiology?
Teleradiology can be used for all types of medical images. It is routinely applied to more common medical imaging —CT scans, MRIs, X-rays, ultrasounds— but can also be used in advanced medical techniques, such as nuclear medicine.
Teleradiology is one of the most advanced niches of telemedicine and one of the easiest to implement. Just as digital technology has replaced film technology in photography, so it has in radiology.
Today’s radiology imaging is entirely digital using PACS (picture archiving and communication system) and DICOM. The American Academy of Radiologists, by way of example, no longer makes a distinction between teleradiology and ordinary radiology, since the present-day standard for the image is the same in both cases. With high speed telecommunications also in place throughout the world today, adequate software applications to share and view the already digital medical images are the only additional pieces needed to implement teleradiology.
How Are Radiological Images Viewed in Teleradiology Applications?
In teleradiology, medical images are seen using a web-based DICOM viewer.
DICOM stands for Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine. It is both a protocol for all hardware and software used in radiology and a file type for storing medical images, such as x-ray and MRI images. A DICOM file, defined as the international standard for storing and transmitting medical images, allows the patient’s information to be integrated into a single file.
A web-based DICOM viewer enables DICOM files to be downloaded, viewed and manipulated so that they can be evaluated by medical professionals and used for diagnosis. The advantage of a web-based DICOM viewer is its flexibility and user-friendliness. With a web-based DICOM viewer, DICOM images can be viewed by the receiver on any computer using just a modern internet browser.
How Is Teleradiology Used in Oncology Clinical Trials?
Oncology trials are one of the highest utilizers of teleradiology. This is not surprising since oncology trials require imaging and the evaluation of images at every stage, particularly for the diagnosis and treatment of solid tumors. Also, all the images must be independently and centrally reviewed. Through teleradiology, a central radiologist can review CT scans of patients to verify tumor location, size, and density. Teleradiology offers the best solution for channeling oncology clinical trial images to a single location for review.
What Teleradiology Software Solution Does Zlynger Provide?
Zlynger offers a modern and cost-effective teleradiology solution, which includes a DICOM imaging server and a web-based viewer. This teleradiology system is highly flexible and ideal for both small clinics and large hospitals. It can be used for patient care and clinical research purposes, connecting a large number of locations and radiologists. Without installing any software in their computers, users can easily log into the platform with a username and password, by using an Internet browser, to see the DICOM images.